Gas extraction is a critical component of the global energy sector, providing essential fuel for industries, homes and transportation. However, this process often involves the extraction of groundwater as a byproduct. Managing this groundwater is vital to ensure environmental safety, regulatory compliance and sustainable operations. This article explores how groundwater is extracted alongside gas, what happens to it, the treatment processes it may undergo, storage methods and the role of Polymaster’s storage solutions. A case study of Santos’ use of Polymaster tanks provides real-world context.
Groundwater and Gas Extraction
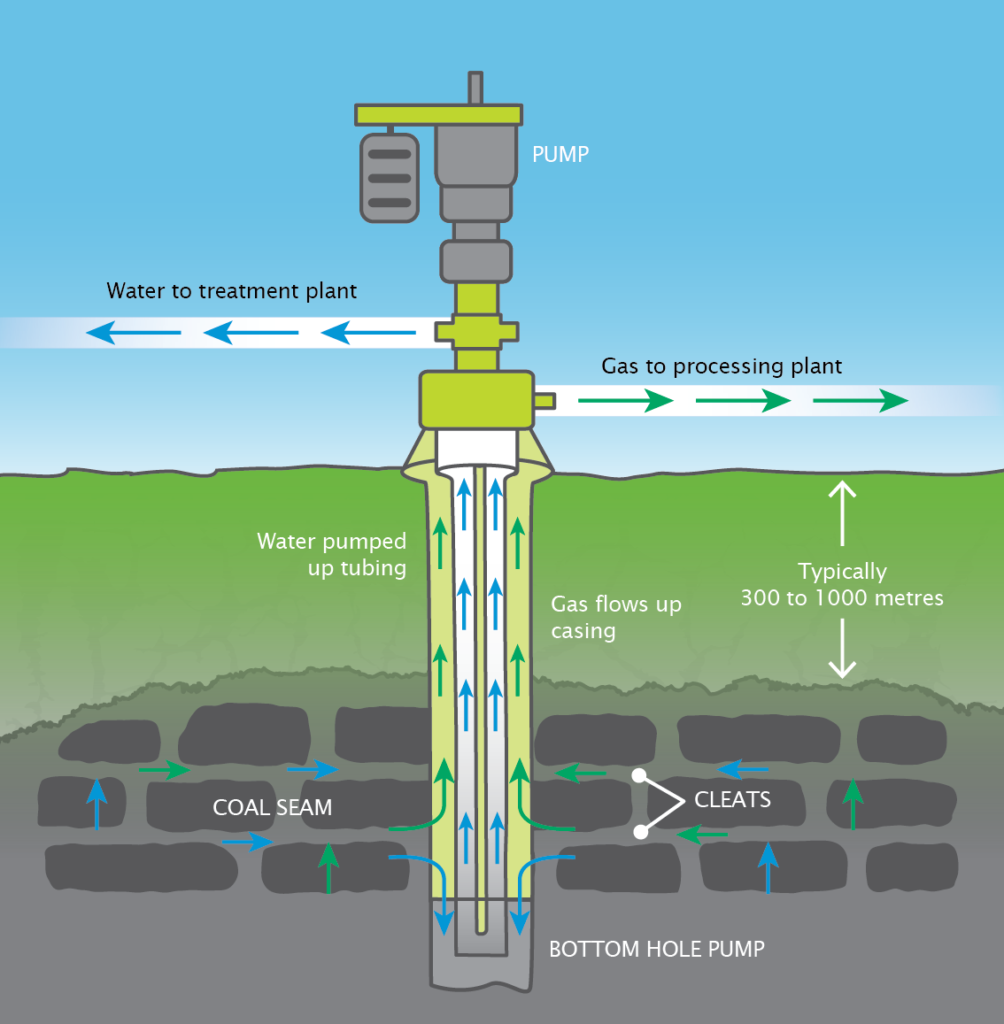
In gas extraction processes, particularly coal seam gas (CSG) and shale gas operations, water naturally present in underground formations is often brought to the surface. This groundwater, also known as produced water, is extracted to reduce pressure in the coal seams or shale formations, allowing the gas to flow freely to the surface.
What Happens to Extracted Groundwater?
Once groundwater is extracted, its management becomes a critical aspect of the gas extraction operation. This water typically contains various dissolved salts, minerals, organic compounds, and sometimes low levels of naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORMs). Depending on its composition and the local regulatory framework, groundwater may undergo one or more of the following processes:
- Treatment: Extracted groundwater often requires treatment to remove impurities and contaminants before it can be reused, discharged or disposed of. Treatment processes may include reverse osmosis, filtration, chemical treatment, or aeration.
- Reuse: Treated groundwater can be reused in agricultural irrigation, industrial processes, or even reinjected into aquifers to support water resources.
- Disposal: If treatment is not viable or the water does not meet reuse criteria, it may be disposed of in evaporation ponds or through deep well injection, depending on regulatory requirements.
Storage of Extracted Groundwater
Before treatment or disposal, extracted groundwater must be stored securely to prevent contamination of soil and nearby water sources. Storage solutions include lined evaporation ponds or tanks. The tanks are generally located at the well pads.
The Role of Polymaster Tanks
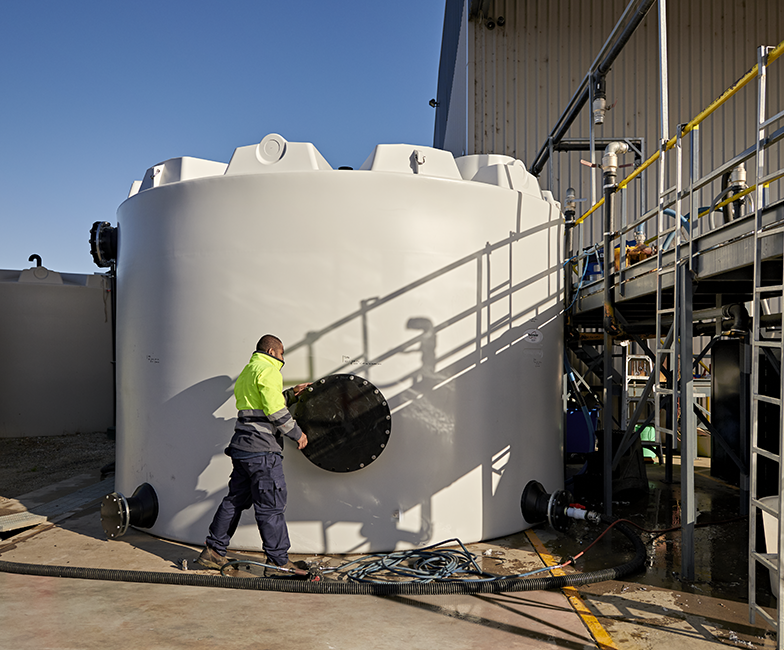
Polymaster tanks are widely recognised for their durability, reliability and ability to store contaminated water safely in demanding industrial environments. Constructed from high-grade polyethylene, these tanks are resistant to corrosion, UV degradation and chemical attack, making them ideal for storing produced water on gas extraction sites. The 50,000L Industrial Process Tank is most used for this application. These heavy-duty industrial tanks have a self-supporting roof which is a must-have, as the groundwater being contained in the tanks holds high levels of dissolved gases, which if released to atmosphere could cause a pole-supported roof to collapse. They can also be customised with unique design features to suit the varying requirements of each gas extraction site.
Case Study: Santos and Polymaster Tanks
Santos, a leading Australian energy company, has been a pioneer in integrating sustainable practices into its operations. At many of its gas extraction sites, Santos utilises Polymaster tanks for the storage of extracted groundwater. The tanks provide a secure and reliable storage solution, ensuring that no environmental contamination occurs while awaiting further processing.
By using Polymaster tanks, Santos was able to meet regulatory standards and reduce environmental risks, highlighting the critical role these tanks play in sustainable gas extraction. These tanks are strategically chosen for their robust design and ability to withstand the harsh conditions of remote gas fields.
Case Study: Santos and Polymaster Tanks
Polymaster collaborated with Santos to develop a customised solution for storing 100,000 litres of groundwater at a gas extraction site in Injune, Queensland. They supplied two 50,000-litre industrial polyethylene tanks with self-supporting roofs to safely contain water with high dissolved gas levels. The project included product development, manufacturing, delivery, and installation. A Santos representative praised Polymaster’s cone system as the best nozzle reinforcement in the Australian rotomoulded tank market.
Conclusion
Groundwater management is a crucial aspect of gas extraction operations. The extracted groundwater must be treated, reused or disposed of responsibly to minimize environmental impacts. Polymaster’s Industrial Process Tanks offer a robust and practical solution for storing this water, ensuring safety and compliance. The case study of Santos demonstrates how these tanks can be effectively used to support sustainable practices in the energy sector. As the demand for energy grows, innovative solutions like Polymaster tanks will continue to play an essential role in balancing industrial needs with environmental stewardship.
Polymaster Chemical Storage & Dosing Projects
More Similar News
View all News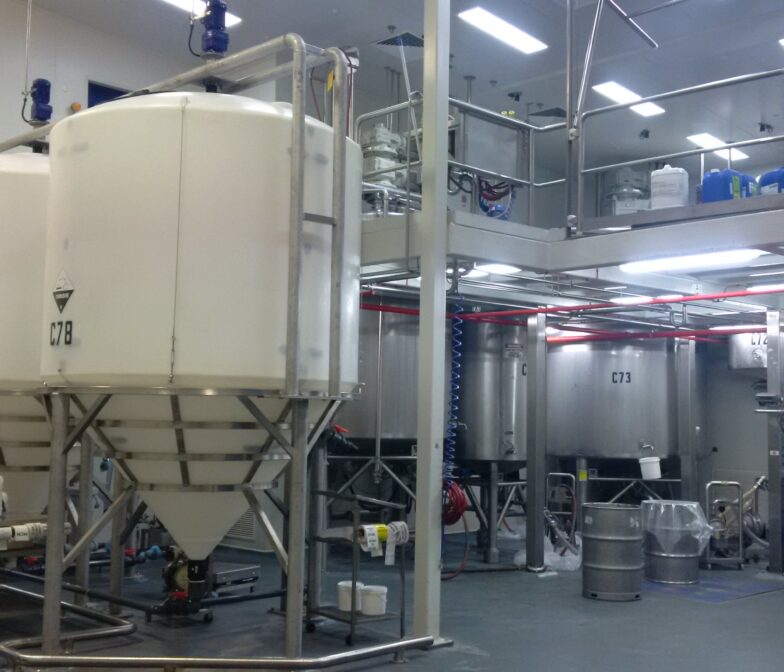
Why Cone Bottom Tanks are Perfect for your Business

The Ultimate Cheat Sheet the Chemical Industry Should Be Using!